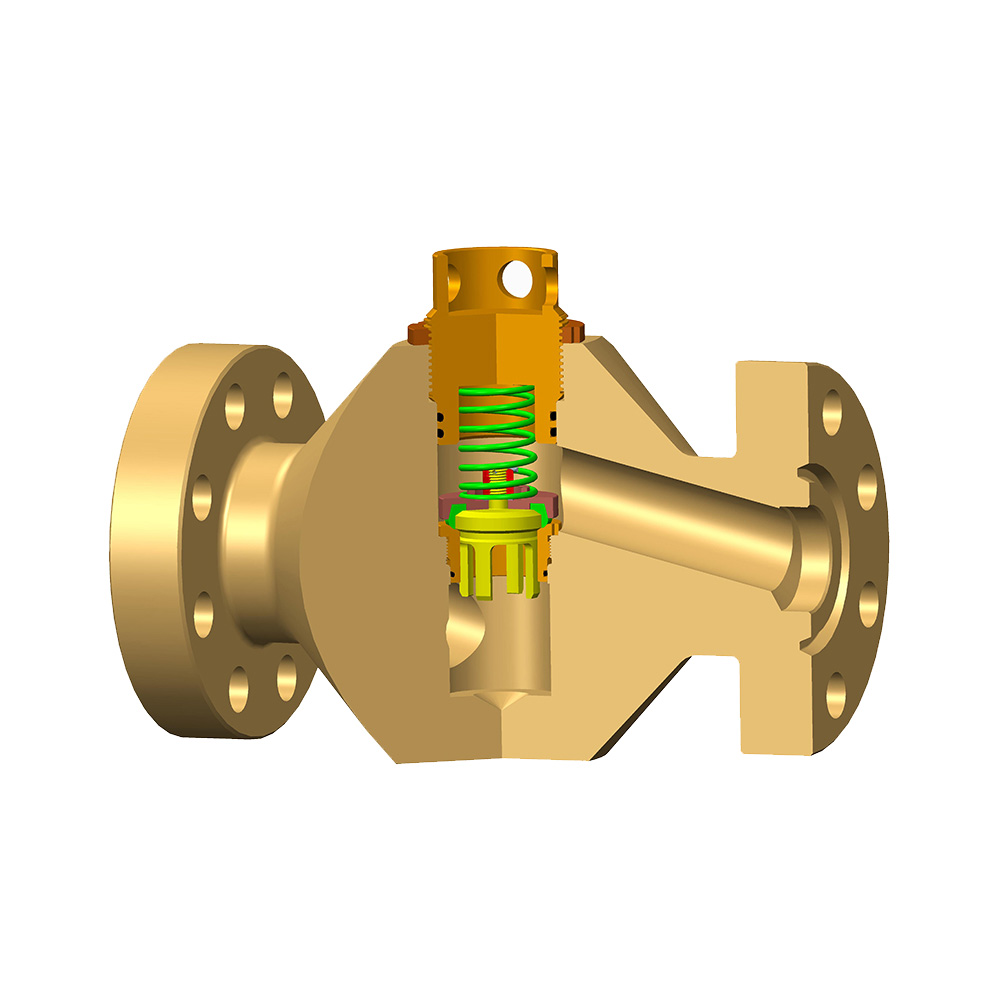
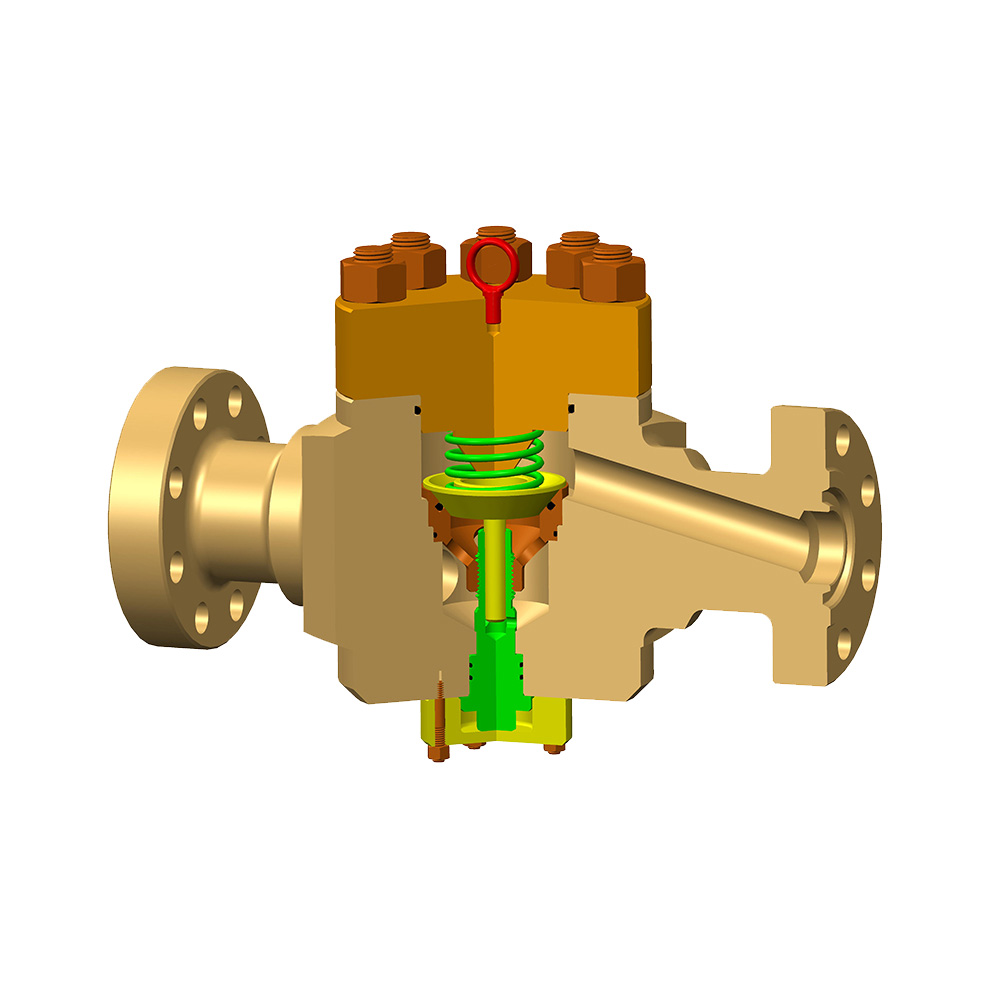
Valves used in oil fields play a crucial role in the process of oil and gas extraction. The following are common valves and their main uses in oil fields:
Control valve: The control valve is used to control the flow rate, pressure, and direction of fluid. In oil fields, control valves are used to regulate wellhead flow, control fluid pressure during water injection and oil production processes, and regulate fluid flow in pipeline systems.
Check valve: A check valve is used to prevent fluid backflow. In oil fields, they are usually installed in pipeline systems to prevent backflow of wellhead fluid and protect the integrity of equipment and pipelines.
Regulating valve: The regulating valve is used to control the flow rate and pressure of the fluid precisely. In the oil field, the regulating valve can be used to regulate the oil well production, water injection pressure, and flow in the pipeline system to meet the requirements of production and operation.
Safety valve: A safety valve is used to protect equipment and systems from damage caused by excessive pressure. In oil fields, safety valves are usually used to control wellhead pressure, prevent equipment explosions, and prevent dangerous situations such as pipeline rupture.
Throttling valve: A throttling valve is used to regulate fluid flow and reduce flow rate. In oil fields, throttle valves can be used to regulate wellhead flow, control oil well production, and reduce fluid velocity when needed to reduce pressure loss and pipeline wear.
Electric valve: The electric valve is automatically controlled through an electric actuator. In oil fields, electric valves are widely used in automation systems to achieve remote operation and monitoring and improve production efficiency and safety.
The application of these valves in oil fields ensures the safety, control, and regulation of fluids while protecting the integrity of equipment and systems. They play a crucial role in the process of oil and gas extraction, ensuring the smooth operation of production.
+86-18066199628
Product Search
Exit Menu
news
News categories
Product categories
RECENT POSTS
-
What are the specific application scenarios of valves in oil fields?
2024-06-01 -
Can the mud gate valve be closed quickly in the event of a blowout?
2024-06-02 -
What are the uses of valves for oil fields?
2024-06-10 -
Welcome to Zhonglin Oil Equipment!
2024-07-08 -
In which industries is GATE VALVE widely used?
2024-09-14
What are the uses of valves for oil fields?
-
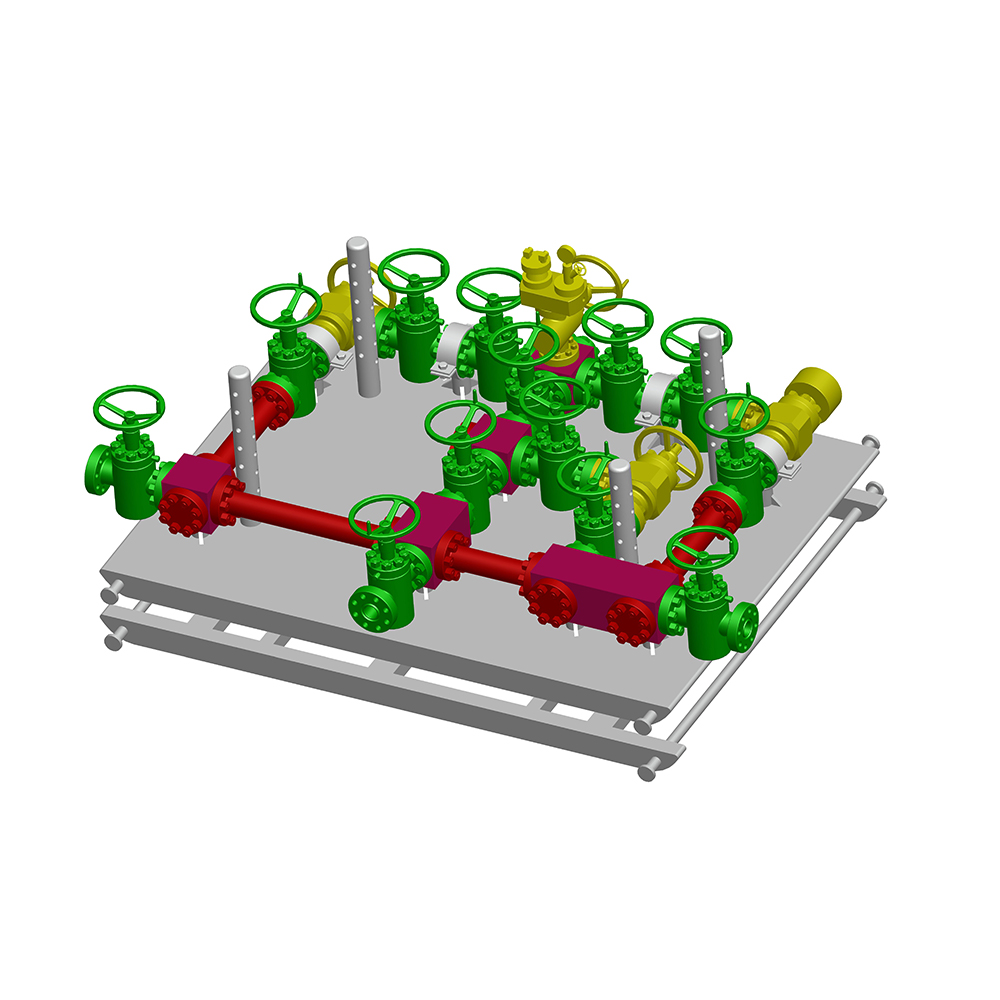
Choke and Kill manifold can effectively control the pressure inside the well and also can control the flow rate of oil gas and mud or other medium which returs from the well when it's used for drillin...
See Details -
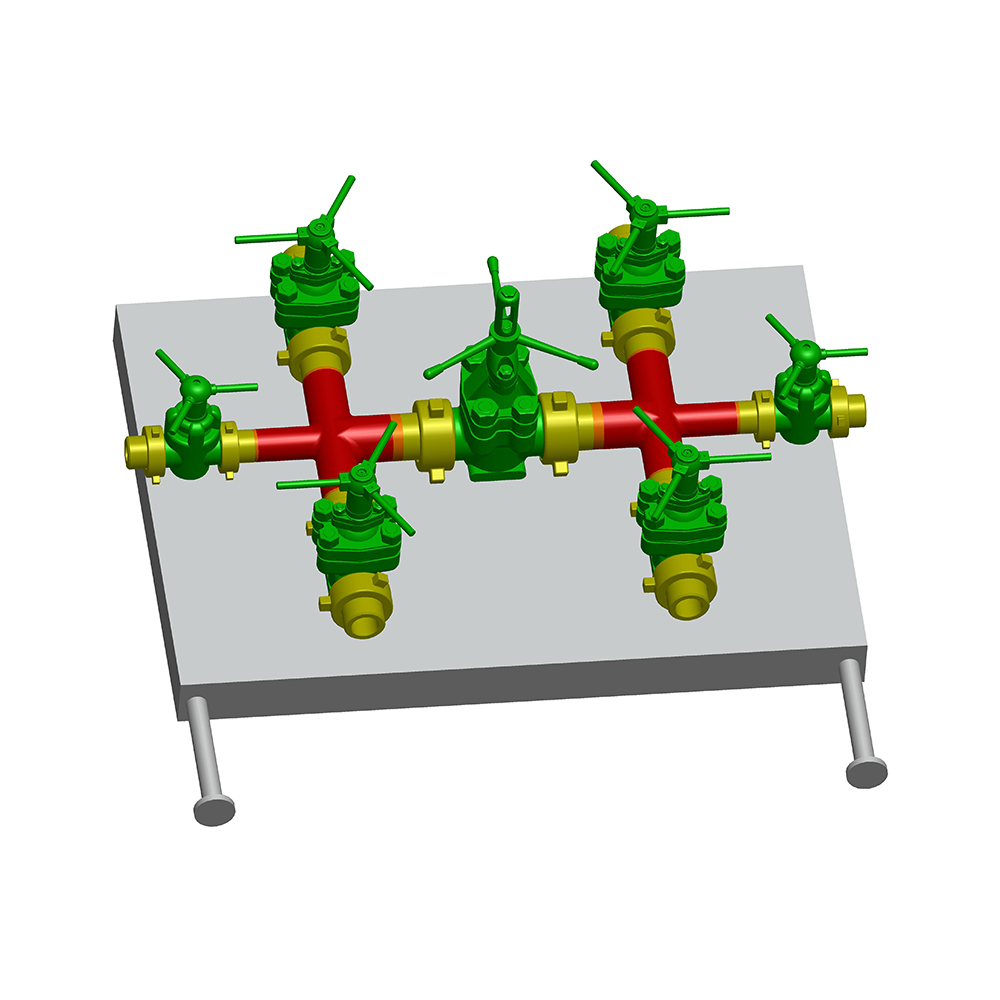
Choke and Kill manifold can effectively control the pressure inside the well and also can control the flow rate of oil gas and mud or other medium which returs from the well when it's used for drillin...
See Details -
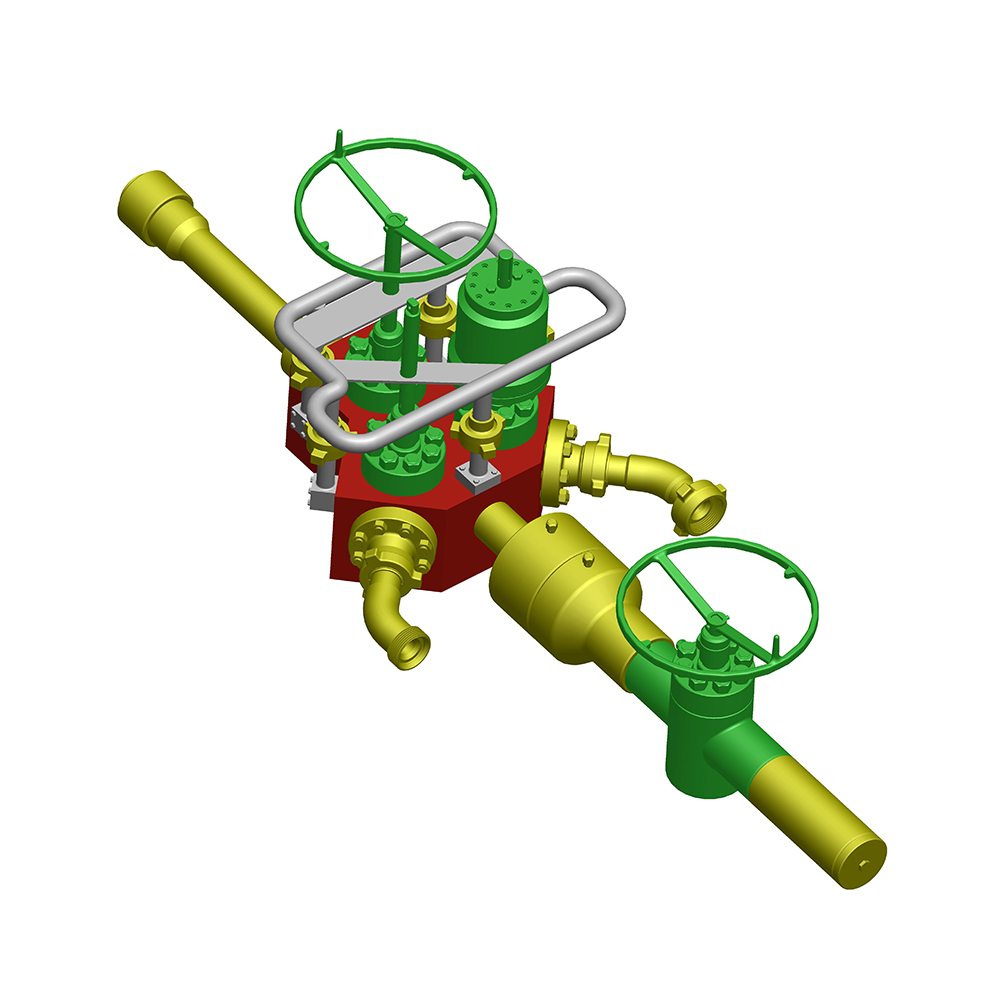
Flowhead sizes:1-13/16" ~9”Pressure Rating:5000psi- 15000psiMax.Tensile Rating:435,000 to 1,500,000 Ibs at 0PSIUpper and lower units are coupled with a load-bearing quick union for easy assembly and d...
See Details -
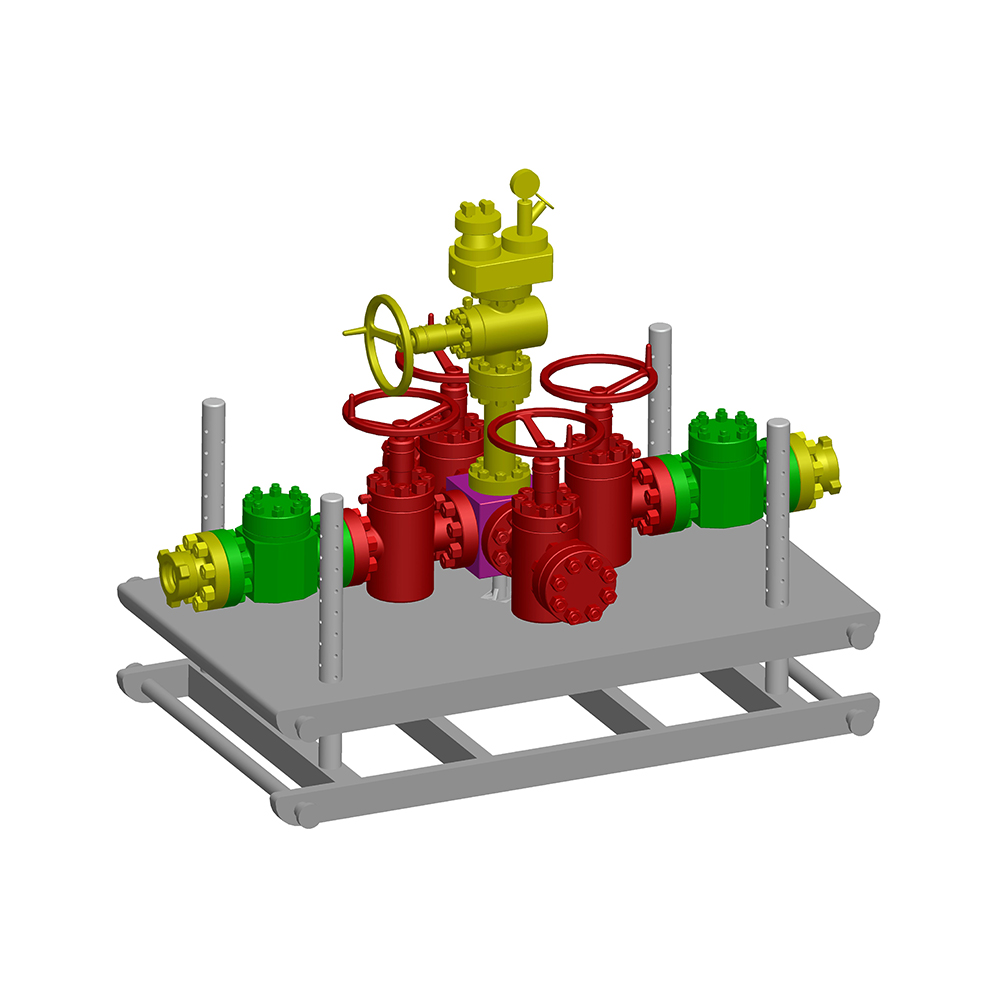
Choke and Kill manifold can effectively control the pressure inside the well and also can control the flow rate of oil gas and mud or other medium which returs from the well when it's used for drillin...
See Details
Contact Zhonglin Support Team for any Inquiry
Mob:
+86-18066199628/ +86-18805110688
Email:
[email protected] / [email protected]
Add: 88 Ronghua Road Yancheng New Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone Yancheng, Jinagsu People's Republic of China