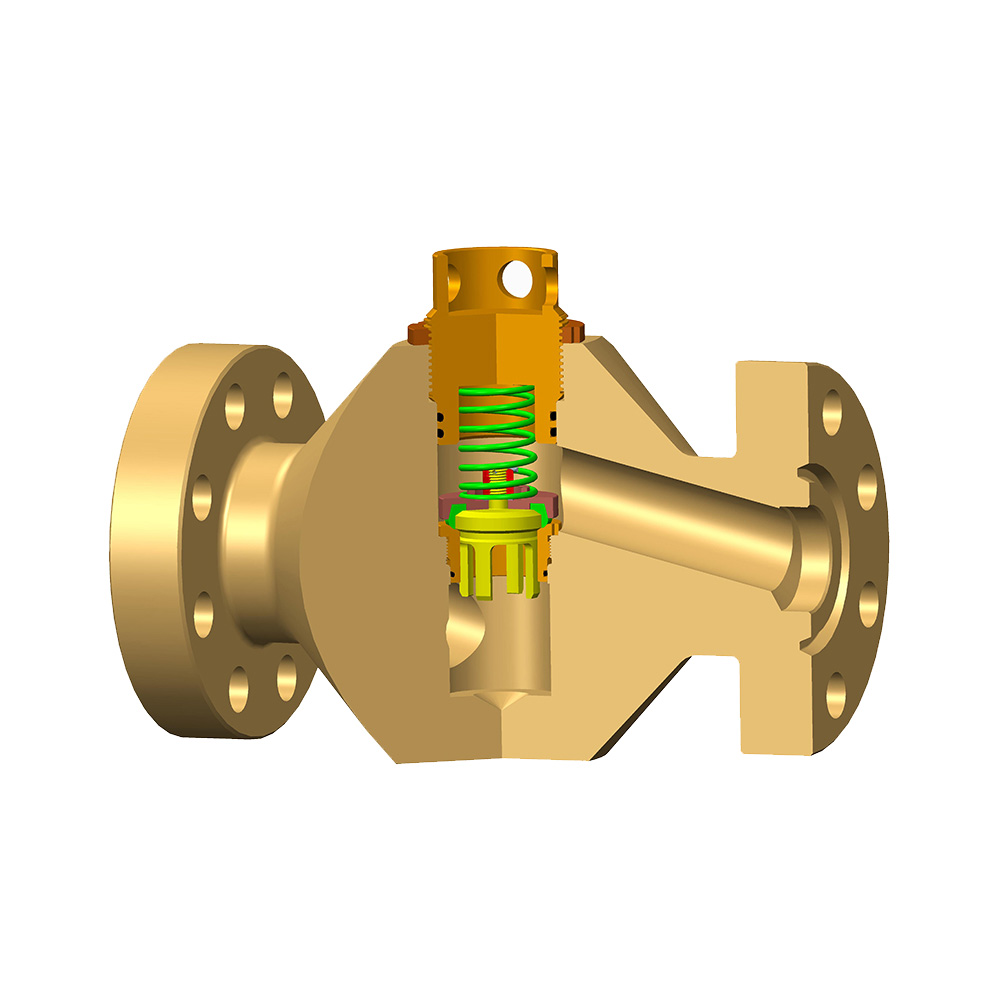
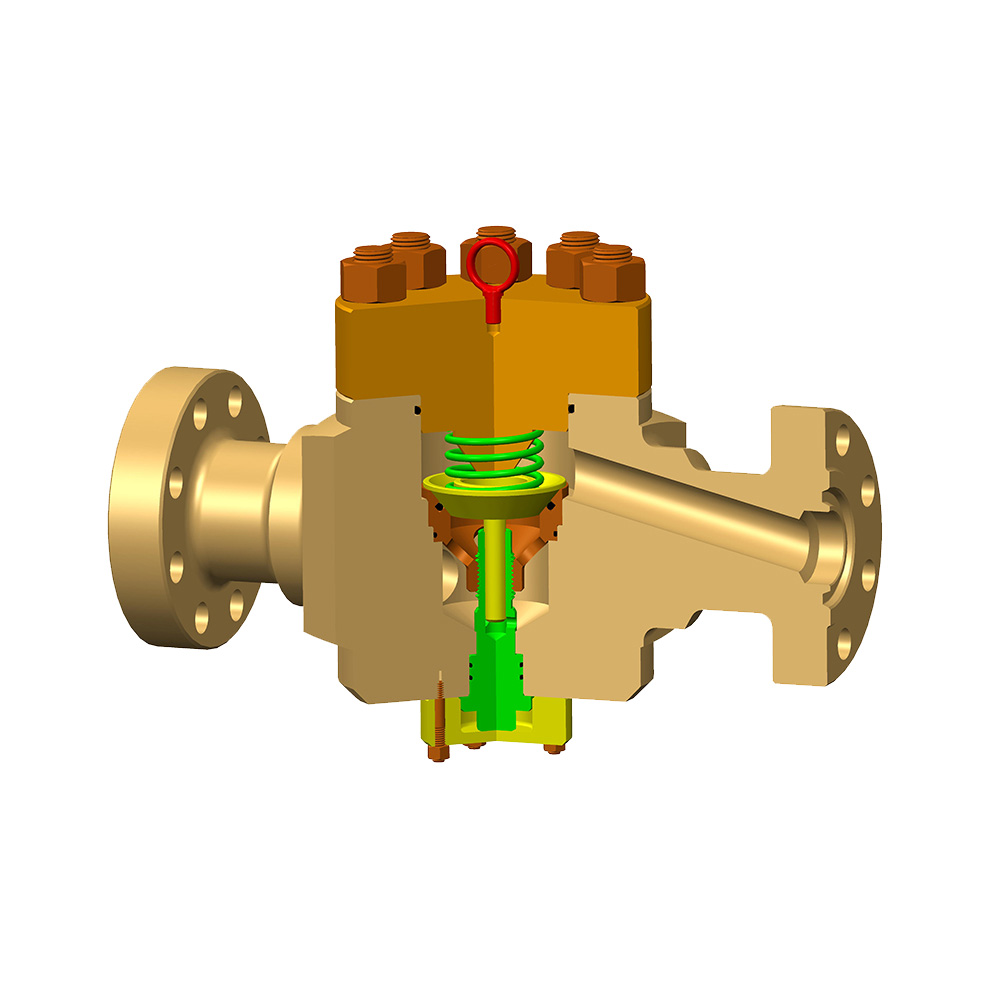
Valves can indeed be used to control fluid pressure, although they typically do so indirectly. The main function of valves is to regulate the flow and direction of fluids, and these adjustments often impact the pressure within a system. Specifically, several types of valves can effectively manage fluid pressure.
Firstly, safety valves are designed specifically for controlling pressure within a system. When the pressure within the system reaches or exceeds the set opening pressure of the safety valve, the valve will automatically open to release excess pressure, thereby preventing overpressure and protecting equipment. Safety valves are protective devices that respond quickly to pressure changes, ensuring that the system operates within safe limits.
Secondly, pressure regulating valves (also known as pressure control valves) are used to directly adjust and maintain pressure within fluid systems. These valves set a target pressure value and automatically adjust their opening to increase or decrease fluid flow when the actual pressure deviates from the set value, keeping the system pressure within the desired range. Pressure regulating valves are commonly used in situations requiring stable pressure, such as in water supply systems, oil and gas processing, and chemical production.
Although throttling valves primarily control fluid flow, they can also indirectly affect system pressure by adjusting flow rates. As fluid flows through a throttling valve, changes in flow rate can lead to pressure changes. For instance, if the valve opening is reduced and flow decreases, the resistance to flow increases, which can cause a rise in system pressure. Conversely, increasing flow may reduce pressure.
In summary, while these valves may not be directly used for pressure control, their regulating functions can influence system pressure. Proper use of these valves allows for precise control of fluid pressure, ensuring the stability and safety of the system.